Lean Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Lean management is a prevalent method that emphasizes continuous improvement. By a methodical and long-term strategy, lean management strives to accomplish progressive development and boost efficiency inside an organization.
The lean management technique was originally established by Toyota in the 1940s as part of the Toyota Production System, and since then, it has been embraced by businesses in a range of industries.
The relevance of lean management in today’s economic landscape cannot be emphasized. Organizations are under constant pressure to become more efficient, productive, and customer-centric due to the intensifying global competition and the diversification of client needs.
Principal Lean Management Principles
The basic principles of lean management are:

- Identify value – Comprehend the customer’s wants and preferences, determine what is important to them, and concentrate on delivering that value.
- Once the value has been established, map out the organization’s value stream, which consists of all the procedures involved in developing and delivering the product or service.
- Continuous workflow – Improve the flow of work in order to reduce waste and increase productivity. Create processes that allow work to flow quickly and efficiently from one phase to the next, without interruptions or delays.
- Pull system — Develop a pull-based system in which goods and services are generated in reaction to client demand, as opposed to in anticipation of it. This aids in minimizing overproduction, reducing inventory, and enhancing response to fluctuating consumer demands.
- Perfection/Continual improvement – Strive for continuous improvement in every facet of the organization. This requires setting lofty objectives, assessing success, and always searching for ways to enhance processes, goods, and services.
Seven Forms of Garbage
“Muda” or waste in Japanese is a seven-category lean management concept for wastefulness. The seven waste types are:
- Overproduction is the process of creating more than is required or too soon, which can result in excess inventory, lost resources, and longer lead time.
- Waiting – Delays or idle time in the production process, such as awaiting materials or a machine’s availability.
- Unnecessary movement or transportation of materials or products, which can increase lead time, raise the danger of damage or loss, and waste resources.
- Over Processing – Doing extra or duplicate processes, or utilizing more resources than necessary, which can increase production costs and duration.
- Inventory – Excess inventory that is not required for immediate production can result in obsolescence and waste, since it ties up money and storage space.
- Excessive or excessive movement of people or equipment, which can be exhausting, time-consuming, and raise the risk of damage.
- Defects — Any faults or mistakes that result in rework or scrap, which adds expense, delays the production process, and can lead to dissatisfied customers.
By detecting and eliminating these types of waste, businesses may improve their operations, save costs, boost efficiency, and raise customer happiness.
The success of lean management is strongly dependent on the participation and collaboration of employees at all levels of the company, as well as their dedication to continuous improvement and their readiness to experiment with new ideas and methods.
Various Lean Management Approaches and Tools
Several lean management tools and approaches are utilized for diverse processes. These are some of the most popular:
5S
s5S is a lean management methodology that stands for its five steps:
- Sort (Seiri) entails dividing items into necessary and useless categories and discarding those that are unnecessary.
- This step involves organizing the necessary items in a logical and effective manner. Everything should have a dedicated place and be easily accessible.
- This process comprises cleaning and maintaining the workplace to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
- Standardize (Seiketsu) – This phase entails developing clear and consistent methods for implementing the first three S’s and defining performance criteria for measuring success.
- This third phase entails making 5S a habit and sustaining the improvements over the long term.
Its primary objective is to produce an orderly, clean, and efficient workplace that reduces waste, boosts productivity, and enhances safety.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a quality management methodology and a data-driven approach to quality control that focuses on reducing process variability and minimizing faults. The DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control) process and the DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) process are the two primary approaches of Six Sigma.
Visual Management
Visual management is a crucial aspect of lean management that employs visual signals such as diagrams, charts, and graphs to create a clear and simple image of the process and its performance. It is essential for communication, standardization, constant improvement, and problem-solving.
Kaizen
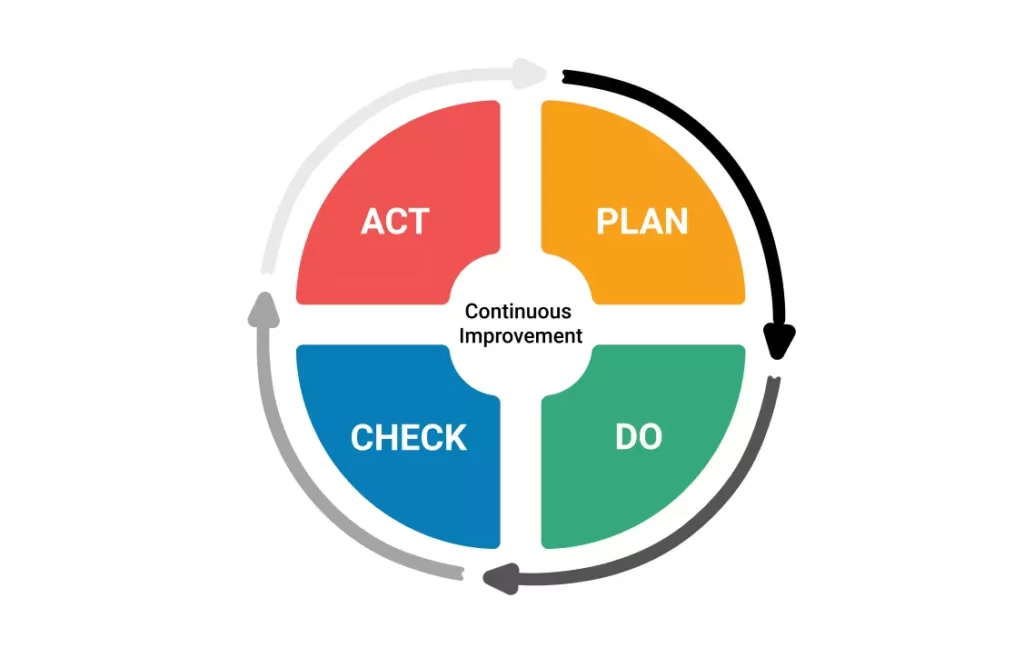
Kaizen is a methodical strategy for continuous development. It focuses on finding and removing waste, decreasing defects, raising productivity, and boosting customer happiness. The Plan, Do, Check, and Act (PDCA) cycle is integral to the Kaizen process, which engages all employees, from top management to various levels. The purpose of Kaizen is to produce incremental improvements inside an organization over time.
SMED
Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED) is a technology used to reduce the time needed to prepare a machine for a different process to less than 10 minutes. This can be achieved by completing as many jobs as feasible while the equipment is still operational and by simplifying, streamlining, and optimizing the remaining procedures.
Kanban
Kanban is a visual management technique frequently employed within the lean management methodology. It is a solution meant to assist firms with workflow management, inventory reduction, and overall efficiency enhancement.
Kanban is based on the “pull” production principle, which means that resources or work items are only produced when required. This helps to prevent excess manufacturing and inventories. In a Kanban system, work items are represented by cards or other visual signals as they go through a succession of stages and processes.
Valuation Flow Mapping (VSM)
VSM is a lean management tool used to assess, plan, and improve the flow of materials and information through a process or system. VSM is a graphical illustration of the phases involved in bringing a product or service from the concept phase to the delivery phase. VSM also identifies waste and inefficiency in a process and develops a plan or strategy to eliminate them.
Crucial Performance Measures (KPIs)
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are crucial metrics utilized in lean management to track and measure progress toward accomplishing particular goals and objectives. KPIs are crucial for assessing the performance of a lean management system and identifying opportunities for development.
Advantages of Lean Administration
Organizations that successfully implement the principles and practices of lean management can enjoy several benefits. These advantages can assist firms in enhancing their operations, decreasing waste, and increasing consumer value. Following are some of the most important advantages of lean management:

- Enhanced productivity – Lean management can enhance productivity by lowering waste and removing superfluous processes stages. Lean management minimizes expenses, shortens lead time, and boosts profitability by streamlining activities and improving their performance.
- Lean management stresses quality, which increases the likelihood that firms will offer products and services that meet or exceed consumer expectations. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as a greater reputation for quality.
- Lean management pushes firms to be more adaptable and nimble in response to market fluctuations. It also enables staff to swiftly detect and resolve issues, allowing organizations to maintain a competitive advantage.
- Increased employee participation – Lean management emphasizes the need to involve employees at all levels in the process of improvement. As a result, engagement, work satisfaction, and morale can increase as employees feel empowered to contribute to the business’s success.
- Cost effectiveness — Companies can achieve considerable cost savings by lowering non-value-added activities and eliminating waste. As resources are made available, they can be invested in expansion, innovation, and other strategic endeavors.
Lean administration and ISO 9001
ISO 9001 provides requirements for the establishment, implementation, operation, and maintenance of a quality management system (QMS). Using ISO 9001 guarantees that clients obtain consistently high-quality products and services, which in turn provides businesses with several advantages.
Lean management and ISO 9001 are distinct methods for enhancing company performance. Yet, they can be complementary, and many organizations have effectively combined the two to achieve their objectives.