Industry 4.0: The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0, often known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is used to conceptualize the current era in which automation and digitization have dominated the industrial industry. It refers to the integration of numerous advanced technologies that are reshaping how individuals and industries function.
Industry 4.0 intends to build smart factories, which are digitalized and contemporary production facilities. They utilize devices, equipment, and systems that are networked and continuously collect and share data utilizing sensors, advanced data analytics, and machine learning algorithms.
The objective of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is to create manufacturing industries that are more flexible, responsive, and customer-centric. With the ability to change the production of products and services, it intends to transform the global economy.
Contextual history of Industry 4.0
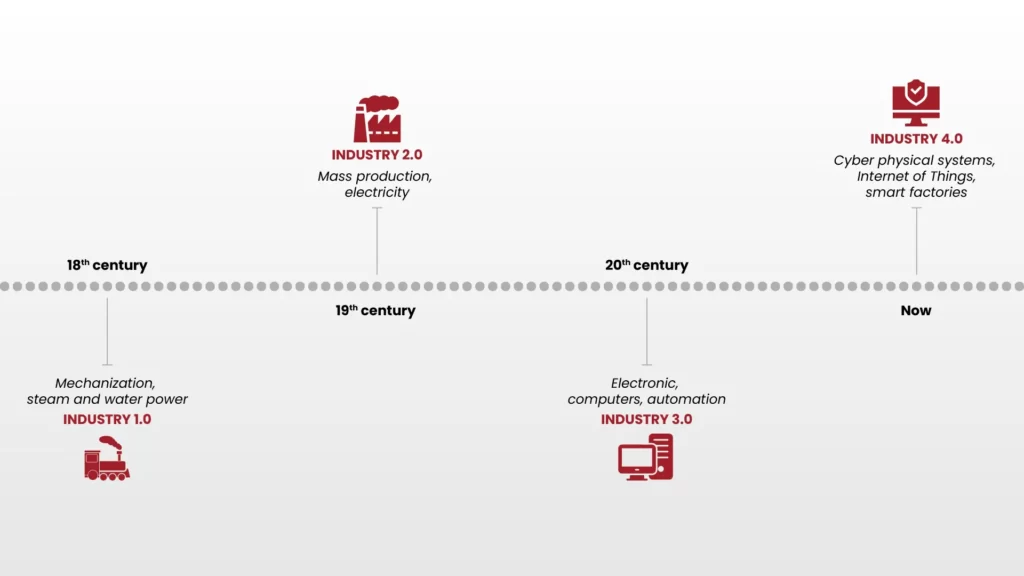
The Primary Industrial Revolution
This period of the First Industrial Revolution lasted from the late 18th century until the middle of the 19th century. It was marked by the shift and modernization of manufacturing processes in Great Britain through the use of water and steam power, which extended to Europe and the United States. This resulted in worldwide economic expansion, the creation of industries, and enhanced productivity and efficiency.
Industrial Revolution II
The Second Industrial Revolution refers to a time from the late 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century. This time was marked by the widespread use of electric power and assembly lines, the rise of new industries, and the expansion of transportation infrastructure such as railroads and steamships, all of which had a profound impact on the lives of the general populace.
Industrial Revolution III
The Third Industrial Revolution, which began in the 1960s and lasted until the end of the 20th century, was characterized by the introduction of new communication systems, information technology, electronics, the internet, and alternative energy sources. This period was also defined by the introduction of computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technologies and the development of computer-controlled machinery.
The Third Industrial Revolution had a major effect on the world, altering the manner in which people work, communicate, and conduct business. Its influence is still evident today in the broad acceptance of new digital technologies that are undergoing transformation.
Industrial Revolution IV
Industry 4.0 or the Fourth Industrial Revolution began in the early 21st century. It is characterized by digitalization, innovation, and the implementation of cutting-edge technology, which result in increasing automation, more efficient production processes, and the creation of new products and services.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is also generating important changes in society and the economy, such as increased connection and access to information, the expansion of the sharing economy, and the emergence of remote and gig employment. Nonetheless, technology also creates significant ethical and social concerns, including as privacy, cybersecurity, and the impact of automation on employment.
The Technology That Drive Industry 4.0
Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger that enables and records safe, transparent, and immutable digital transactions. It has an impact on Industry 4.0 by contributing to it in a number of ways:
- Blockchain offers real-time tracking of goods and transactions, which provides supply chain management with transparency, security, and efficiency.
- Decentralized Manufacturing – Blockchain enables the creation of decentralized manufacturing systems in which machines may connect and perform transactions autonomously.
- Data Security — Using cryptography and ensuring that only authorized parties can access the data, Blockchain can provide secure data storage and sharing. This can help safeguard sensitive data and lessen the likelihood of data breaches.
- Digital Identity — Using blockchain, identity systems may verify users and offer access to a variety of services and resources. This can assist in preventing identity theft and decreasing fraud.
Artificial Intelligence
AI has changed Industry 4.0 by enabling computers to examine data, learn from it, make judgments, and perform activities that previously required human intelligence. This can result in increased production, efficiency, and quality.
For instance, AI may evaluate sensor data from manufacturing equipment to discover process optimization potential. Additionally, it can detect anomalies and predict problems before they occur. This permits preventive maintenance and decreases downtime.
Practical Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that permits users to interact with virtual worlds. Professionals can utilize virtual reality to simulate and visualize complicated goods and processes, discover potential design flaws early on, and make more educated decisions.
Workers can use VR for training and skill development since they can practice doing activities in dangerous conditions without endangering others. Moreover, VR enables workers in different locations to cooperate in shared virtual spaces.
Digital Twin
A digital twin is a replica of a physical product or system that is utilized to imitate, monitor, and optimize its performance. Digital twins are utilized in Industry 4.0 to generate virtual representations of physical production processes and acquire real-time insights about the functioning of their physical systems.
Robotics
Robotics can be utilized to automate and perform a variety of functions in Industry 4.0. As an example, robots can be used to perform welding, painting, and assembly. They work quickly, precisely, and ceaselessly, which makes them ideal for repeated or dangerous tasks. Collaboration between humans and robots can result in more flexible and efficient industrial processes. In addition, robots sort and move packages in warehouses, enhancing the speed and reliability of the supply chain.
Cloud Technology
Industry 4.0 relies on cloud computing to store, process, and analyze massive quantities of data from machines, sensors, and other sources in a cost-effective and scalable manner.
Cloud computing is predominantly employed in Industry 4.0 for data storage and administration, analytics and machine learning, remote monitoring and control, and collaboration and communication.
The Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that allows physical items and gadgets to send and receive data over the internet. In Industry 4.0, the IoT is used to link machines, sensors, and other devices in order to build more efficient and integrated industrial processes. For instance, IoT can be used to monitor equipment performance and manage inventory levels.
Cybersecurity
Considering many of Industry 4.0’s interconnected advanced technologies are vulnerable to cyberattacks, cybersecurity is a crucial problem. Industry 4.0’s utilization of networked devices and systems increases the number of attack vectors available to cybercriminals. Industry 4.0 manufacturers must build strong cybersecurity plans to handle these challenges. In addition, they must remain current on the most recent cybersecurity threats, best practices, and policies and attend cybersecurity awareness workshops.
Characteristics of Industry 4.0
Four important elements of Industry 4.0 are as follows:
- Vertical Integration – Industry 4.0 can integrate vertically all stages of the production process, from raw materials to finished goods. This connection integration enables for improved process coordination and optimization.
- Horizontal Integration – By integrating processes horizontally, Industry 4.0 might facilitate more collaboration and communication across different departments, suppliers, and customers.
- End-to-End Engineering — In addition to focusing just on how a product is manufactured, Industry 4.0 emphasizes end-to-end engineering, which considers how the product will be utilized and discarded.
- Industry 4.0 is characterized by the rapid growth of manufacturing, which is possible by the application of several technologies.
Overall, Industry 4.0 has significantly enhanced the manufacturing industry. With the appropriate approach, the Fourth Industrial Revolution may continue to fuel growth and innovation while also building a more equal and inclusive society, despite concerns about the potential effects of new technology.